DeFi Staking Explained: From Concept To Risks And Security

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has revolutionized the way we think about financial services, and at the heart of this transformation lies staking. Staking is the most attractive financial solution, with billions of dollars locked in staking contracts. This article delves deep into the world of DeFi staking, offering a comprehensive guide from its basic concepts to the intricate details of risks and security. You'll find valuable insights into what DeFi staking is, how it works, its various types, benefits, and potential risks to consider.
Join us as we unravel the complexities of DeFi staking and explore its role in shaping the future of finance.
What Is DeFi Staking?
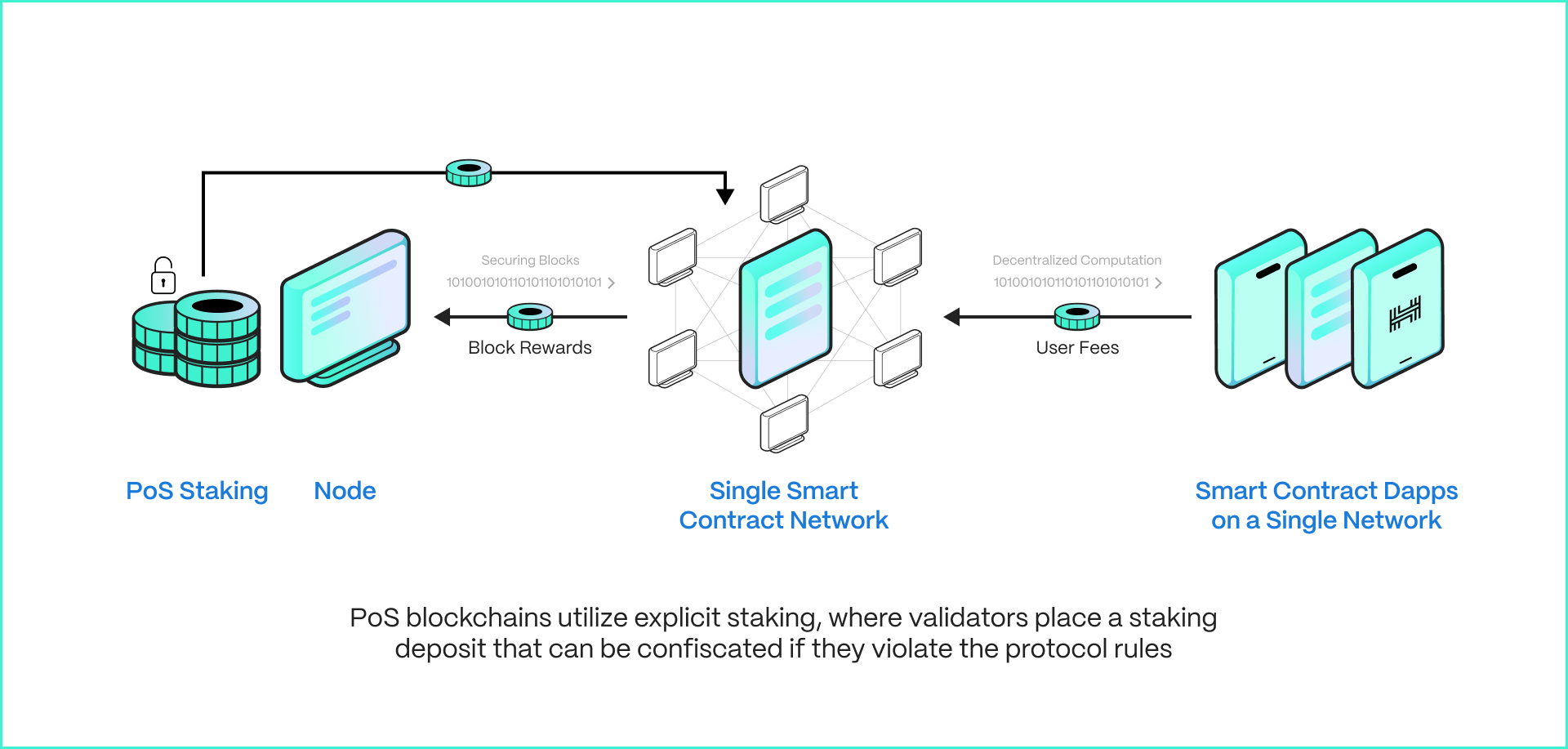
To understand staking, one should be aware of the purpose of the underlying blockchain: to ensure consensus of transactional data and network security. The first iteration of blockchains, primarily Bitcoin, used the Proof-of-Work (POW) consensus mechanism, where “work,” meaning computational power, was the foundation. In more recent blockchain architectures, Proof of Stake (POS) has become the most widely adopted consensus mechanism. Here, staked assets locked in contracts are the foundation of consensus and security.
Participants lock up their assets to support the operations of a blockchain network. In return for their contribution, stakers earn rewards, typically through additional tokens.
This process serves a dual purpose:
- It provides a way for token holders to earn passive income on their crypto assets.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining the security and integrity of blockchain networks that use a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
DeFi staking is essentially a more accessible and decentralized version of traditional financial practices like earning interest on savings accounts or stock dividends. It also allows individuals to participate directly in the network's operations and governance, embodying the core principles of decentralization and community participation that define the DeFi ecosystem.
How DeFi Staking Works
The underlying mechanics of staking can be broken down:
- Proof of Stake (PoS): This is the underlying consensus mechanism. PoS selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they're willing to "stake" as collateral.
- Validators: These are network participants who have staked tokens and are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. They earn rewards for their service but can also be penalized for malicious behavior.
- Staking Process:
- Users lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a compatible wallet or staking platform.
- The staked tokens are then used to support network operations, either directly or through a staking pool.
- As the network processes transactions and creates new blocks, stakers earn rewards proportional to their stake.
- Staking Pools: Pools allow smaller token holders to combine their resources for networks with high staking requirements. The pool operator manages the staking process and distributes rewards proportionally to participants.
- Lock-up Periods: Many staking arrangements require tokens to be locked for a certain period. During this time, the staked assets cannot be transferred or sold.
- Rewards Distribution: Staking rewards are typically distributed automatically by the network or staking platform, often on a regular schedule (e.g., daily or weekly).
By participating in this process, stakers contribute to the network's security and efficiency while earning rewards for their involvement.
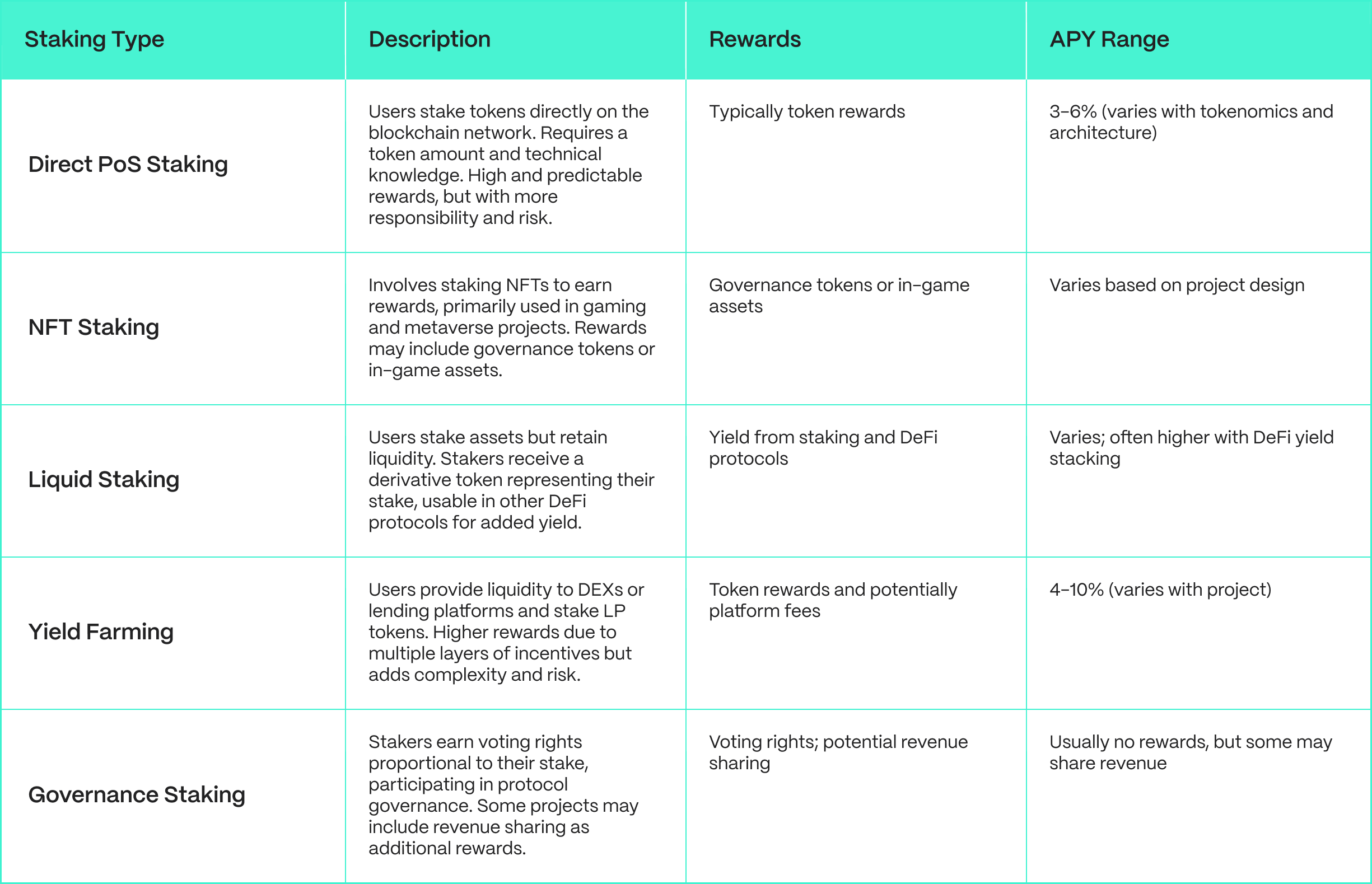
Types of DeFi Staking
While the main type of staking has been to provide security and ensure consensus of underlying networks, new forms of DeFi staking have arisen each with its own characteristics and use cases: